ISO 9001 QMS supplier and vendor register Template
A robust supplier and vendor register is crucial for implementing an effective Quality Management System (QMS) in accordance with the ISO 9001 standard. This register ensures that organizations have complete visibility and control over their supply chain, allowing them to identify, evaluate, and monitor the performance of their suppliers and vendors. A well-maintained register helps improve the quality of products and services and reduces the risk of non-compliance and customer dissatisfaction. This blog post will explore the importance of a QMS supplier and vendor register and provide practical tips for creating and managing one effectively.

The Importance of Having Suppliers and Vendors Register.
The importance of having a supplier and vendor register cannot be stressed enough when it comes to implementing an effective Quality Management System (QMS) in accordance with the ISO 9001 standard. This register plays a crucial role in ensuring that organizations have complete visibility and control over their supply chain, allowing them to identify, evaluate, and monitor the performance of their suppliers and vendors.
One of the key benefits of having a robust supplier and vendor register is that it helps improve the quality of products and services. By maintaining a register, organizations can have a clear overview of their suppliers and vendors, including their capabilities, certifications, and performance history. This allows them to make informed decisions when selecting and approving suppliers and vendors, ensuring that only those who meet the organization's quality requirements are chosen.
Additionally, a well-maintained supplier and vendor register helps reduce non-compliance risk. Organizations can ensure that they adhere to regulatory and quality standards by thoroughly evaluating and monitoring suppliers and vendors. This helps prevent potential non-compliance issues from using suppliers or vendors who do not meet the required standards.
Furthermore, having a supplier and vendor register helps mitigate the risk of customer dissatisfaction. By carefully selecting suppliers and vendors based on their performance history and capabilities, organizations can ensure they deliver high-quality products and services to their customers. This, in turn, helps build customer trust and loyalty, increasing customer satisfaction.
Creating and managing a supplier and vendor register effectively requires a systematic approach. Organizations should establish transparent supplier and vendor evaluation criteria, such as quality certifications, delivery performance, and customer feedback. They should also regularly review and update the register to ensure its accuracy.
The importance of having a supplier and vendor register cannot be overlooked when implementing an effective QMS. It helps improve the quality of products and services, reduces the risk of non-compliance, and enhances customer satisfaction. Organizations can effectively monitor and control their supply chain by creating and managing a well-maintained register, leading to better overall quality management.
Key Components of the Supplier and Vendor Register Includes
Certainly, let's expand on each of the key components for a Supplier and Vendor Register:
1. Supplier ID: The Supplier ID is a unique identifier for each supplier or vendor in your system. It simplifies record-keeping and makes it easier to track and reference supplier-related information. This ID may be alphanumeric and can be generated internally by your organization's system.
Implementing a Supplier ID system requires careful planning and coordination with stakeholders within the organization. Establishing clear guidelines and procedures for assigning and managing Supplier IDs is essential. Regular updates and maintenance of the Supplier ID system will help to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness in supporting the supplier and vendor management process.
2. Supplier/Vendor Name: The supplier/vendor’s name is a key component of the QMS (Quality Management System) supplier and vendor register. It refers to the supplier or vendor's official name or business name being added to the register. Capturing accurate and complete supplier/vendor names in the register is essential for effective supplier management and ensuring traceability in the supply chain process.
3. Contact: The Contact section includes details for key personnel responsible for communication and coordination at the supplier or vendor organization. This typically includes names, job titles, email addresses, phone numbers, and mailing addresses. Having reliable contact information ensures smooth communication and issue resolution.
4. Product/Service: In this section, specify the products or services the supplier or vendor provides. Include a detailed description of what they supply to your organization, including product specifications or service scope. This clarity helps in understanding the supplier's role in your supply chain.
5. ISO 9001 Certified: Indicate whether the supplier/vendor holds ISO 9001 certification. This certification demonstrates their commitment to implementing and maintaining a quality management system that aligns with ISO 9001 standards. It's essential to ensure that suppliers meet your quality expectations.
6. Evaluation Criteria: By evaluating suppliers and vendors based on these criteria, organizations can ensure that they select partners who can maintain the highest standards of quality and contribute to their overall quality management system. Regular monitoring and evaluation of suppliers and vendors should also be performed to ensure ongoing compliance and continuous improvement.
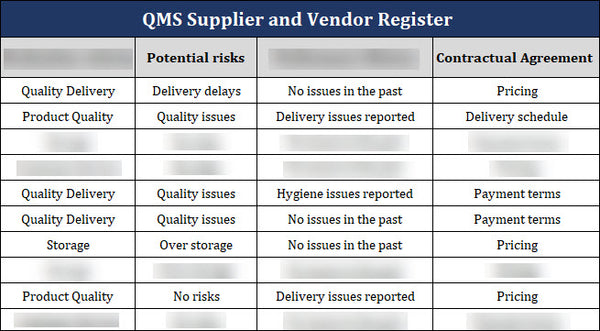
7. Potential Risks: To mitigate these potential risks, organizations should implement risk management strategies such as conducting thorough evaluations, establishing strong contractual agreements, monitoring supplier and vendor performance, and maintaining open lines of communication. Proactive risk management can help organizations maintain the highest standards of quality and ensure the success of their ISO 9001 certification.
8. Performance History: When selecting QMS suppliers and vendors for ISO 9001 certification, it is essential for organizations to evaluate their performance history thoroughly. By assessing their track record and past performance, organizations can make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks. Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating the performance history of potential suppliers and vendors:
9. Contractual Agreement: Once an organization has thoroughly evaluated the performance history of potential QMS suppliers and vendors for ISO 9001 certification, it is essential to establish clear and transparent contractual agreements. These agreements outline the rights and responsibilities of both parties involved, ensuring that expectations are communicated and any potential risks are mitigated.
Common Challenges in Maintaining a Supplier and Vendor Register
While creating a supplier and vendor register is crucial for effective supply chain management, organizations often face challenges maintaining and updating this register. Some common challenges include:
1. Data Accuracy and Timeliness: Ensuring the accuracy and timeliness of supplier/vendor information can be a challenge. Suppliers and vendors may change their contact details, product offerings, or certifications, which need to be updated in the register promptly. Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to miscommunication, delays, and quality issues.
2. Supplier/Vendor Evaluation: Regular supplier/vendor performance evaluation is essential for maintaining quality standards. However, conducting comprehensive performance evaluations can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Organizations may struggle to allocate sufficient resources for evaluating each supplier/vendor effectively.
3. Risk Assessment and Monitoring: Assessing and monitoring supplier/vendor risks requires continuous effort and vigilance. Identifying and addressing potential risks, such as financial instability, regulatory non-compliance, or changes in business practices, can be challenging. Proactive risk management is crucial to mitigate any negative impact on product quality and customer satisfaction.
4. Contractual Compliance: Keeping track of contractual agreements, including terms and conditions, pricing details, and service level agreements, can be challenging. Organizations must ensure that contractual obligations are met by both parties and that any necessary updates or amendments are documented and implemented.
5. Supplier/Vendor Development: Encouraging supplier/vendor development requires ongoing communication and collaboration. Organizations may face challenges tracking supplier/vendor improvement activities and ensuring alignment with their quality management objectives. Establishing a framework for supplier/vendor development and monitoring progress can be complex.
6. Non-Conformance Management: Managing non-conformances or quality issues related to suppliers and vendors requires a systematic approach. Organizations need to document and analyze non-conformance records to identify trends, root causes, and areas for improvement. This process can be time-consuming and may require coordination with multiple stakeholders.
Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive and systematic supplier and vendor management approach. Organizations can effectively maintain and update their supplier and vendor register by implementing robust processes, leveraging technology solutions, and fostering strong communication and collaboration with suppliers and vendors, ensuring a streamlined and high-quality supply chain.
Conclusion
Establishing clear and transparent contractual agreements with QMS suppliers and vendors is crucial for ensuring clarity and transparency in the ISO 9001 certification process. These agreements outline the rights and responsibilities of both parties involved, define the scope of work, specify quality requirements, detail pricing and payment terms, address intellectual property rights and confidentiality, including a dispute resolution mechanism, and establish mechanisms for performance monitoring and evaluation.
Organizations can mitigate potential risks by having well-defined contractual agreements, clearly communicating expectations, and maintaining a positive working relationship with their QMS suppliers and vendors. These agreements provide a roadmap for collaboration and help safeguard the organization's interests throughout the certification process.



