ISO 9001 Non-Conformities and Corrective Actions Management Template
Effective nonconformities and corrective action management are crucial for organizations seeking compliance with ISO 9001, a widely recognized quality management standard. Nonconformities, or deviations from specified requirements, can occur in any organization and significantly impact product quality, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance. ISO 9001 provides a framework for identifying, documenting, analyzing, and addressing nonconformities and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence. This blog post will explore the key principles and best practices for nonconformities and corrective action management in ISO 9001, helping organizations achieve and maintain high-quality standards.
Understanding Non-Conformities in ISO 9001
In ISO 9001, nonconformity refers to any deviation from the requirements or standards specified in the quality management system. Understanding nonconformities is important for ensuring compliance with the ISO 9001 standard and improving overall quality.
Here are some key points to understand about nonconformities in ISO 9001:
1. Definition: A nonconformity is the non-fulfilment of a requirement found during an audit, inspection, or review. It can be a failure to meet a specific standard, a lack of documentation, or a deviation from established procedures.
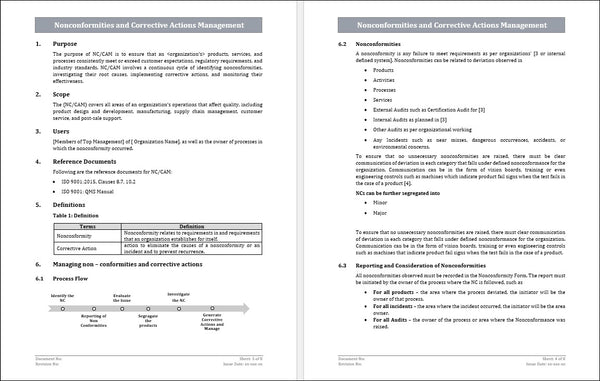
2. Types of Non-Conformities: Nonconformities can be major or minor, depending on their impact on the quality management system. Major nonconformities significantly impact the system's ability to achieve its objectives, while minor nonconformities have a lesser impact.
3. Identification and Documentation: Nonconformities should be identified, documented, and recorded in a nonconformity report or log. The report should include details such as the nature of the nonconformity, its location, and any evidence supporting the findings.
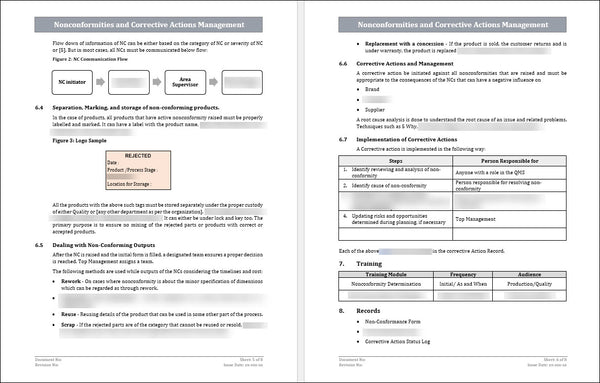
4. Root Cause Analysis: Whenever a nonconformity occurs, it is important to conduct a root cause analysis to determine the underlying cause. This involves investigating the reasons behind the nonconformity and taking corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
5. Corrective and Preventive Actions: Corrective actions address already occurring nonconformities, while preventive actions are implemented to prevent future recurrence of similar nonconformities. These actions should be appropriate, effective, and documented.
6. Review and Follow-Up: Nonconformities should be reviewed during management reviews, and their effectiveness should be monitored and evaluated. This helps to ensure that the necessary actions have been taken and the nonconformities have been resolved.
7. Continuous Improvement: The management of nonconformities is an integral part of the ISO 9001 continuous improvement process. Organizations can learn from their mistakes and improve their quality management system by identifying and addressing non-conformities.
In summary, understanding nonconformities in ISO 9001 is essential for maintaining compliance with the standard and continuously improving the quality management system. Organizations can ensure conformity to requirements and enhance overall quality performance by identifying, investigating, and taking appropriate actions.
The Importance of Corrective Actions
Corrective actions play a crucial role in the ISO 9001 nonconformities management process. By taking prompt and effective corrective actions, organizations can address the root causes of nonconformities and prevent their recurrence. This ensures compliance with ISO 9001 requirements and improves overall business performance.
Corrective actions can help organizations identify and eliminate process inefficiencies, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. It enables the organization to continually improve its quality management system by learning from nonconformities and implementing preventive measures. Furthermore, a proactive approach to corrective actions demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement, which can lead to increased customer trust, loyalty, and market competitiveness.
Instructions to Use the Template
All yellow indicated numbers in the Nonconformities and corrective actions management need action. Below are the details:
1. Provide the Revision History of the document
Revision Number: in the order of 00,01,02, etc.
Date: Revision Date of Document in dd-mmm-yyyy
Prepared By: Name of the person who prepared the document.
Reviewed By: Name of the person who reviewed the document after revision.
Approved By: Name of the person who approved the document after revision.
Description: Describe the revision
2. Insert Company Name
3. Type either of the below as applicable
IMS – Integrated Management system i.e., ISO 9001:2015, 14001:2015, 45001:2018 all
QMS – Quality Management system, i.e., ISO 9001:2015
EMS – Environmental Management system, i.e., ISO 14001:2015
OHSMS – Occupational Health and Safety Management System i.e., ISO 45001:2018
4. Can add as being followed by the Organization
5. Add any other category as per the Organization
6. Add to the list as per the Organization’s working module, can modify as per requirement
7. Sample NC Communication flow displayed in Figure 2, modified as per Organization
8. Sample Rejected Tag shown in Figure 3, modified as per Organization
9. Add the applicable audience as per the Organization
10. Modify as per the Organization.
Monitoring and Measuring the Success of Corrective Actions
Once corrective actions have been implemented, organizations must monitor and measure their effectiveness. This step is crucial to ensure that the actions taken have successfully addressed the root causes of the nonconformities and prevented their recurrence.
To monitor and measure the success of corrective actions, organizations can establish key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with their quality objectives. These KPIs can include metrics such as the number of nonconformities resolved, the time to implement corrective actions and the reduction in repeat incidents.
Regular audits and inspections can also be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the corrective actions. These audits can identify potential gaps or areas for improvement in the nonconformities management process, allowing organizations to make necessary adjustments to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 requirements.
In addition to internal monitoring and measurement, organizations should consider seeking feedback from customers and other external stakeholders. This feedback can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of corrective actions and help identify any areas of improvement.
By effectively monitoring and measuring the success of corrective actions, organizations can ensure that their nonconformities management process is robust and continuously improving. This commitment to continuous improvement will address current nonconformities and prevent future ones, enhancing customer satisfaction and overall business performance.
Continuous Improvement in Non-Conformities Management
To ensure the sustained effectiveness of corrective actions in ISO 9001 compliance, organizations must adopt a culture of continuous improvement in their nonconformities management process. This means constantly reviewing and revising the process to identify areas for enhancement and implement necessary changes.
One way to continuously improve is by analysing the data collected during the monitoring and measurement. By carefully examining the KPIs and other metrics, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern. This analysis can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of corrective actions and help prioritize improvement efforts.
Organizations should also encourage a proactive approach to nonconformities management. This involves empowering employees to report and address nonconformities promptly and promoting a culture of learning from mistakes and sharing best practices. By fostering an open and collaborative environment, organizations can tap into their workforce's collective knowledge and expertise to continuously improve their nonconformities management process.
Another important aspect of continuous improvement is staying updated with the latest developments in ISO 9001 and other relevant quality management standards. Organizations should regularly review and update their nonconformities management procedures to align with changes in the standards and industry best practices.
Conclusion
To conclude, a culture of continuous improvement is crucial for effective nonconformities and corrective action management in ISO 9001 compliance. By analysing data and metrics, organizations gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their actions and can prioritize improvement efforts. Encouraging a proactive approach that empowers employees to report and address nonconformities promptly fosters a collaborative environment that promotes learning and sharing best practices. Staying current with the latest developments in ISO 9001 and regularly reviewing and updating nonconformities management procedures are also essential for success.



