ISO 9001 Internal Audit Procedure Template
Internal audit is a critical component of the ISO 9001 quality management system. It serves as a systematic and independent examination of an organization's internal processes, procedures, and systems to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards and identify areas for improvement.
An effective internal audit procedure is vital for organizations seeking ISO 9001 certification, as it demonstrates their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. In this blog, we will delve into the key aspects of the internal audit procedure in ISO 9001, providing valuable insights and practical tips for implementing an effective audit program. Whether SO 9001 or looking to enhance your existing audit procedures, this blog is a must-read for quality management professionals seeking to optimize their internal audit process.
The Importance of Internal Auditing in ISO 9001
Internal auditing plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of an ISO 9001 quality management system. It provides organizations with an objective assessment of their processes, identifying strengths and weaknesses to guide improvements. By conducting regular internal audits, organizations can ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards and continuously enhance their quality management processes.
One of the key benefits of internal auditing is its ability to detect non-conformances before they become significant issues. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities early on, organizations can prevent the occurrence of customer complaints, costly errors, and reputational damage. Additionally, internal audits allow organizations to stay updated with changing industry trends and regulations, helping them to adapt and improve their processes as required.
Furthermore, internal auditing fosters accountability and transparency within an organization. It encourages staff members to take ownership of their roles and responsibilities, knowing their work will be evaluated through the audit process. This leads to a cut continuous improvement culture, where employees constantly seek to enhance their performance and meet quality objectives.
In conclusion, internal auditing is an essential component of ISO 9001, enabling organizations to maintain a high level of quality and continually improve their processes. The following section will explore the key steps in conducting an effective internal audit within the ISO 9001 framework. Stay tuned for valuable insights and practical tips on implementing a successful internal audit program.
The Key Components of an Internal Audit Procedure
It looks like you've outlined some key components of an internal audit procedure in the context of ISO 9001. Let me elaborate on each of these components:
1. Responsibilities:
- Members of the Organization: Define the roles and responsibilities of various personnel within the organization concerning the internal audit process. This includes individuals from different departments who may be involved in or affected by the audit.
- Director Auditing and Inspection: Specify the responsibilities of the Director Auditing and Inspection. This individual may oversee the entire internal audit process, ensuring its effectiveness and compliance.
- Internal Audit Team Leader: Clearly outline the responsibilities of the Internal Audit Team Leader, who is crucial in coordinating and leading the internal audit activities.
2. Conducting an Internal Audit:
- Internal Audit Planning: Establish a systematic approach to planning internal audits. This involves determining the scope, objectives, and criteria for the audit. Plan the audit schedule, resources, and any necessary training.
- Appointing Internal Auditors: Define the process for selecting and appointing internal auditors. This may include criteria for auditor competence, independence, and impartiality.
- Internal Audit Reports: Detail the procedures for conducting the actual audit, including gathering evidence, interviewing personnel, and documenting findings. The format and content of internal audit reports should be standardized and meet ISO 9001 requirements.
- Follow-up Activities: Outline the steps for addressing non-conformities or areas for improvement identified during the audit. This may include corrective and preventive actions, as well as monitoring and verification of their effectiveness.
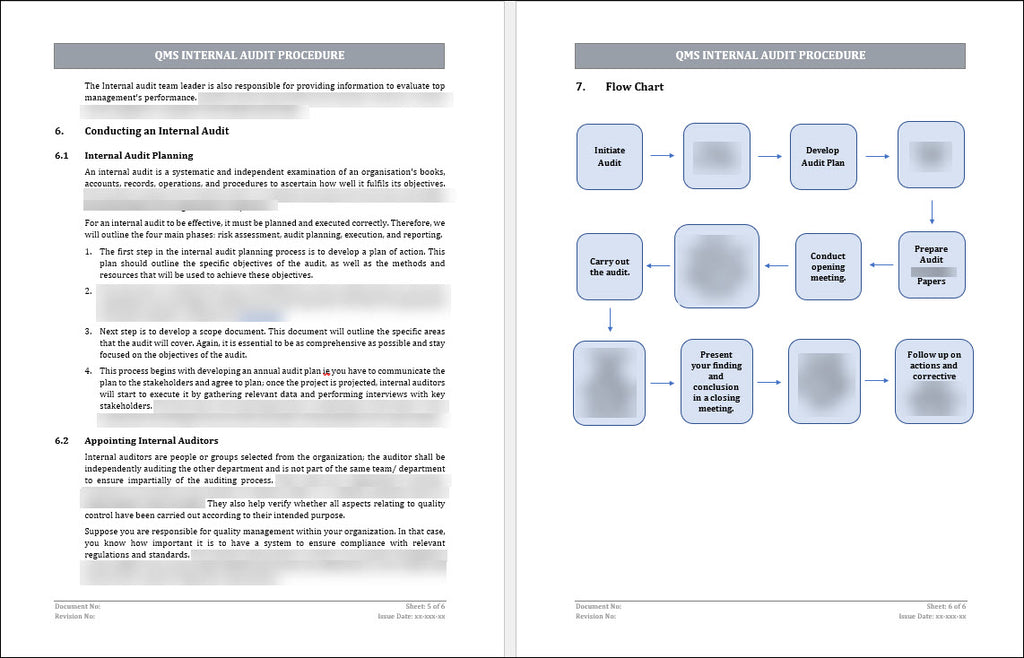
3. Flow Chart:
Flow Chart for the Internal Audit Process: Create a visual representation of the entire internal audit process using a flow chart. It should include key steps such as planning, conducting the audit, reporting, and follow-up. The flow chart helps stakeholders understand the sequence of activities and their interrelationships.
Remember, the internal audit procedure should align with the principles of ISO 9001, emphasizing continual improvement, customer satisfaction, and the effectiveness of the quality management system. Regular reviews and updates to the internal audit procedure ensure its relevance and effectiveness over time.
Continuous Improvement Through Internal Auditing
Organizations must prioritize continuous improvement to maximize the benefits of internal auditing within the ISO 9001 framework. Through regular internal audits, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement effective practical actions.
- The first step in continuous improvement is establishing clear internal audit objectives. These objectives should align with the organization's overall quality goals and provide a basis for evaluating the effectiveness of the quality management system.
- Once the objectives are established, the next step is to plan the internal audit. This involves determining the scope of the audit, selecting the audit team, and developing an audit plan that outlines the audit activities and timeline.
- During the audit, the team will gather evidence and assess the organization's compliance with ISO 9001 requirements. This may involve interviews with staff members, review of documents and records, and observation of processes in action.
- After completing the audit, the audit team must analyze the findings and identify areas for improvement. This includes identifying non-conformances or opportunities for enhancing the effectiveness of the quality management system.
- The organization can develop and implement corrective actions based on the findings and analysis. These actions may include revising procedures, providing additional training to staff members, or implementing new processes to address identified weaknesses.
- Finally, organizations should monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions and evaluate the results. This may involve conducting follow-up audits to ensure that the identified issues have been resolved and that the quality management system is functioning effectively.
By following these key steps and committing to a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can unlock the full potential of internal auditing within the ISO 9001 framework. Stay tuned for the next section, where we will dive deeper into these steps and provide practical tips for implementing a successful internal audit program.
Conclusion
To conclude, implementing a robust internal audit procedure is essential for organizations seeking to achieve and maintain ISO 9001 certification. Organizations can ensure their quality management system is effective and aligned with their overall goals by prioritizing continuous improvement and following the key steps outlined in this blog.
Throughout this blog, we have discussed the importance of establishing clear objectives for internal audits, planning the audit process, gathering evidence, analysing findings, implementing corrective actions, and monitoring their effectiveness.
The following section will delve deeper into these steps, providing practical tips and best practices for implementing a successful internal audit program. We will explore how to set objectives that are measurable and aligned with organizational goals, how to select an effective audit team, and how to conduct thorough audits that provide valuable insights for improvement.



