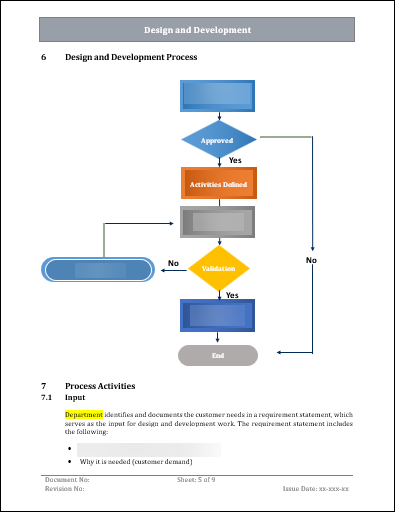
The Design and Development Plan Template for ISO 9001 is a crucial document that outlines the steps and processes involved in designing and developing products or services for ISO 9001 certification. It helps organizations create a structured plan that meets ISO 9001 requirements, defines objectives, and allocates resources. The template covers key components such as risk management, verification and validation, design changes, and document control. It also helps identify and address risks and opportunities for improvement. Overall, the template enhances the quality and reliability of products and services while increasing customer satisfaction.
Understanding The Importance Of An ISO 9001 Design And Development Plan
An ISO 9001 design and development plan is essential in ensuring that an organization's products or services meet the needs and expectations of customers. It helps mitigate risks, improve processes, and drive innovation. Here are some key reasons why an ISO 9001 design and development plan is important:
1. Customer Satisfaction: By following a well-defined design and development plan, an organization can consistently deliver high-quality products or services that meet customer requirements. This helps in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Risk Management: The design and development plan includes an evaluation of potential risks and mitigation strategies. It helps in identifying and addressing potential problems early in the process, reducing the likelihood of costly errors or failures.
3. Process Improvement: A design and development plan provides a structured approach to improve processes. It ensures that best practices are followed and that lessons learned from previous projects are incorporated into future designs. Continuous improvement is essential for enhancing overall organizational performance.
4. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations and standards that must be met for product or service design and development. An ISO 9001 design and development plan helps ensure compliance with these regulations, reducing the risk of legal and regulatory issues
5. Increased Efficiency: A well-documented design and development plan streamlines the process, reducing redundancy and improving efficiency. It ensures that teams are working towards a common goal and minimizes confusion or delays.
6. Innovation: The design and development plan encourages organizations to adopt a forward-thinking approach and fosters innovation. It allows for the exploration of new ideas and technologies, enabling organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving business environment.
7. Accountability And Traceability: An ISO 9001 design and development plan provides clear guidelines and responsibilities for each stage of the process. This promotes accountability and ensures that activities are traceable, facilitating effective communication and coordination between different teams or departments.
Overall, an ISO 9001 design and development plan is important for organizations to ensure consistent quality, manage risks, comply with regulations, improve efficiency, foster innovation, and enhance customer satisfaction. It serves as a roadmap for designing and developing products or services that meet the highest standards.
Key Components Of An Effective Design And Development Plan
1. Clear Goals And Objectives: A design and development plan should have well-defined and measurable goals and objectives that align with the overall project or business objectives. These goals should be specific, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
2. Comprehensive Research And Analysis: Before starting the design and development process, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and analysis to understand the target audience, market trends, user needs, and competitors. This research should inform the design and development decisions.
3. User-Centered Design Approach: An effective design and development plan should prioritize the needs and preferences of the end-users. It should involve user research, user personas, and user testing to ensure that the final product or solution meets their expectations and solves their problems.
4. Iterative Design And Development Process: Developing a design and development plan that includes an iterative approach ensures that the project progresses in small, manageable stages. Each stage should include prototyping, user testing, and feedback loops, allowing for continuous refinement and improvement.
5. Clear Project Scope And Timeline: A well-defined project scope outlines the boundaries, deliverables, and expectations of the design and development process. Additionally, a realistic project timeline helps manage expectations and ensures all stakeholders are aware of the project's timeframes.
6. Cross-Functional Collaboration: Effective design and development plans involve collaboration between different teams and disciplines, such as designers, developers, marketers, and stakeholders. This collaboration helps ensure a holistic and well-rounded approach to the project, incorporating diverse perspectives and expertise.
7. Technology And Resource Allocation: The plan should specify the technology stack, software tools, hardware requirements, and budget for the design and development process. Resource allocation, such as assigning the right team members with relevant skills and expertise, is essential for efficient and successful implementation.
8. Testing And Quality Assurance: An effective plan includes a robust testing and quality assurance process to identify and fix any issues or bugs in the design and development stages. It should involve functional and non-functional testing, usability testing, and adherence to industry standards and best practices.
9. Documentation And Knowledge Transfer: Proper documentation of the design and development process is crucial for knowledge transfer and future maintenance of the product or solution. This includes design specs, style guides, code documentation, and other relevant documentation necessary for future reference.
10. Continuous Improvement And Evaluation: An effective design and development plan should incorporate mechanisms for continuous improvement and evaluation. This includes collecting and analyzing feedback, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), and incorporating lessons learned into future iterations or versions of the product.
Best Practices For Implementing And Maintaining The Plan For ISO 9001
Implementing and maintaining the design and development plan for ISO 9001 requires following certain best practices to ensure effectiveness and compliance. Here are some key recommendations:
1. Understand The Requirements: Thoroughly comprehend the ISO 9001:2015 standard's requirements related to design and development activities. This includes sections 8.3 and 8.4, which outline the specific criteria, processes, and evaluations required.
2. Establish Design And Development Processes: Develop well-defined and documented processes for design and development activities. This includes clear steps to ensure requirements are understood, risks are assessed, inputs/outputs are clearly defined, and verification/validation activities are conducted.
3. Define Roles And Responsibilities: Clearly assign roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability throughout the design and development process. This includes design authorities, project managers, engineers, reviewers, and approvers, among others. Clearly communicate and document these roles.
4. Training And Competence: Ensure personnel involved in design and development activities possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their assigned tasks. Provide appropriate training, maintain competence records, and conduct periodic reviews to identify training needs.
5. Document Control: Establish a robust document control system to manage all design and development-related documents and records. This system should ensure that effective version control, distribution, retrieval, and revision control are maintained. Also, document any changes made during the design and development process.
6. Risk Management: Incorporate risk management methodologies into the design and development process. Identify and evaluate potential risks associated with design changes, product realization, and delivery. Develop appropriate mitigation plans and monitor risk levels throughout the development lifecycle.
7. Reviews And Audits: Conduct regular reviews and audits to verify compliance with design and development processes, ISO 9001 requirements, and customer specifications. These reviews and audits should provide objective evidence of effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
8. Feedback And Continuous Improvement: Establish mechanisms to capture feedback from stakeholders, including customers, during the design and development process. Use this feedback to improve future designs and identify opportunities for continuous improvement
9. Control Of Nonconformities: Establish a process to identify, report, and address nonconformities identified during the design and development process promptly. Implement corrective actions to address the root causes and prevent recurrence.
10. Management Review: Include design and development activities in the organization's management review process. This ensures that top management is aware of the progress, performance, and effectiveness of the design and development plans.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively implement and maintain their design and development plans in compliance with ISO 9001 requirements, leading to improved product quality, customer satisfaction, and business performance.
Conclusion
Design and development play a crucial role in achieving ISO 9001 certification. The design and development processes should be well-documented, controlled, and continuously improved to meet the requirements of the standard. To achieve this, organizations should establish a structured approach to design and development that includes clear objectives and requirements, effective planning, risk assessment and mitigation strategies, and clear communication and collaboration between relevant stakeholders. It is essential to involve relevant parties, such as customers, suppliers, and employees, in the design and development processes to gather their input and ensure their needs and expectations are met.